2021.03.31 - [전체글] - 자료구조 공부#10 (수식의 계산)
큐(QUEUE)
먼저 들어온 데이터가 먼저 나가는 자료구조(스택과 순서가 반대된다)
2021.03.07 - [이론공부/자료구조] - 자료구조 공부 #1 (자료구조와 알고리즘)
자료구조 공부 #1 (자료구조와 알고리즘)
# 자료구조란 무엇일까? 자료구조는 컴퓨터용어로 설명을 하자면 스택, 리스트, 큐, 사전, 그래프 등의 데이터를 표현하는 형식을 말하는것이다. 일상생활에 비유하여 표를 만들어 설명을하자면
thesauro.tistory.com
위에 이전글 참고하면 일상에 예시로 알 수 있다.
큐의 추상적 구조
- 객체 : 0개 이상의 요소들로 구성된 선형 리스트
- 연산 :
- Creat(max_size) ::= 최대 크기가 max_size인 공백 큐를 생성
- init(q) ::= 큐를 초기화
- is_empty(q) ::= if (size == 0) then return true; else return false;
- is_full(q) ::= if (size == max_size) then return true; else return false;
- enqueue(q, e) ::= if (is_full(q)) queue_full 오류; else q의 끝에 e를 추가한다.
- dequeue(q) ::= if( is_empty(q)) queue_empty 오류; else q의 맨앞에 있는 e를 제거하여 반환한다.
- peek(q) ::= if (is_empty(q)) queue_empty 오류; else q의 맨앞에 있는 e를 읽어서 반환한다.
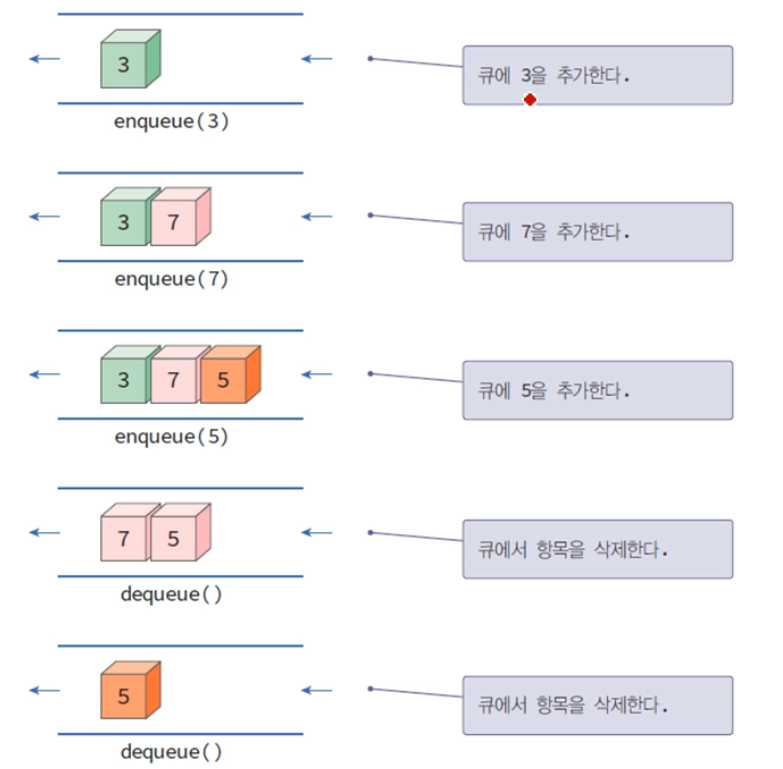
응용 용도
- 시뮬레이션 대기열(공항 비행기, 은행 대기열)
- 통신에서의 데이터 패킷들의 모델링에 이용
- 프린터와 컴퓨터 사이의 버퍼링
- 간접적응용
- 스택과 비슷하게 이용
- 많은 알고리즘에서 사용
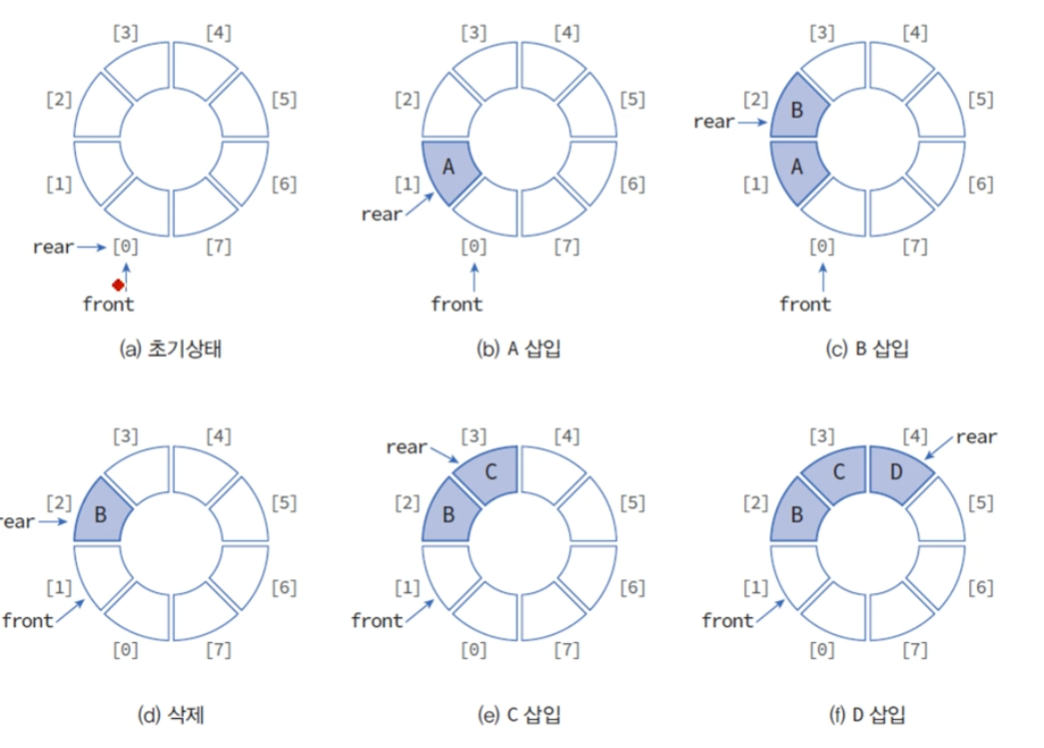
선형 큐(Liner Queues)
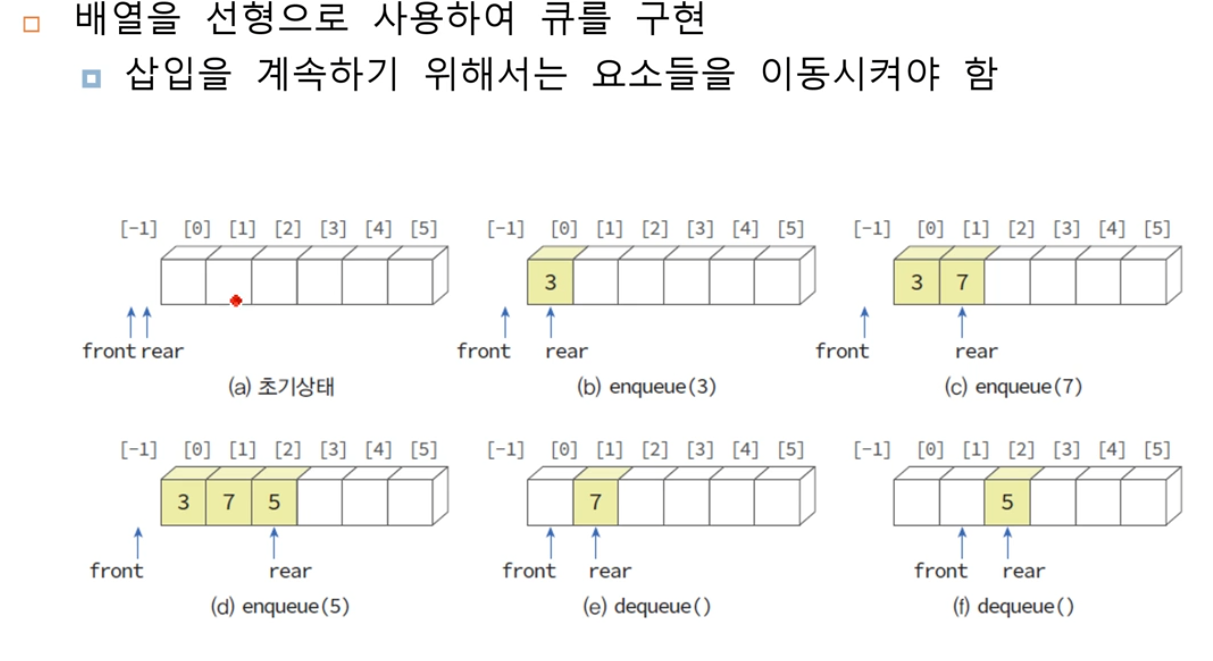
큐에서는 스택과 다르게 삽입된 데이터는 그후 삽입을 위해서는 요소를 이동시켜야 한다.
그림 4번째에서는 이미지가 약간 다른데 front는 7 앞을 가르켜야하고 rear는 그뒤를 가르켜야 한다.
C로 큐(queue) 타입 구현하기
더보기
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 5
//queue 구조체
typedef int element;
typedef struct{
int front;
int rear;
element data[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
} QueueType;
//에러 메세지 출력
void error(char *message){
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", message);
exit(1);
}
//초기화
void init_queue(QueueType * q){
q->rear = -1;
q->front = -1;
}
// QUEUE 타입 출력 함수
void queue_print(QueueType *q){
for(int i = 0; i<MAX_QUEUE_SIZE; i++){
if (i <= q->front || i> q->rear){
printf (" |");
} else{
printf("%d | ", q->data[i]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int is_full(QueueType *q){
if (q->rear == MAX_QUEUE_SIZE -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int is_empty(QueueType *q){
if (q->front == q->rear)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
void enqueue(QueueType *q, int item){
if (is_full(q)){
error("큐가 포화 상태입니다.");
return;
}
q->data[++(q->rear)] = item;
}
void dequeue(QueueType *q){
if (is_empty(q)){
error("큐가 공백 상태 입니다.");
return -1 ;
}
int item = q->data[++(q->front)];
return item;
}
int main(void){
int item = 0;
QueueType q;
init_queue(&q);
enqueue(&q, 10); queue_print(&q);
enqueue(&q, 20); queue_print(&q);
enqueue(&q, 30); queue_print(&q);
item = dequeue(&q); queue_print(&q);
item = dequeue(&q); queue_print(&q);
item = dequeue(&q); queue_print(&q);
return 0;
}
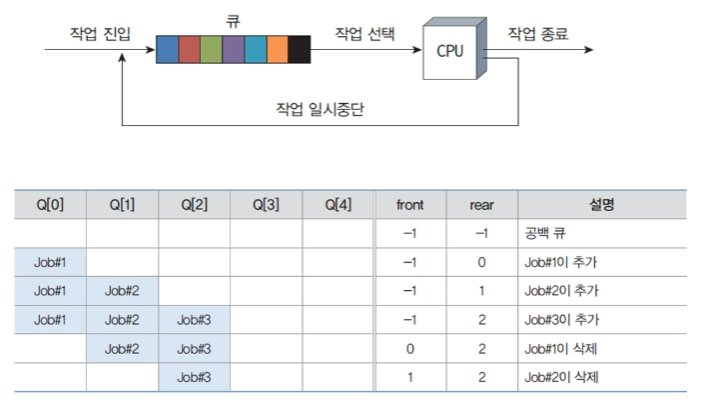
선형 큐의 응용 : 작업 스케쥴링
원형 큐(Circular Queues)
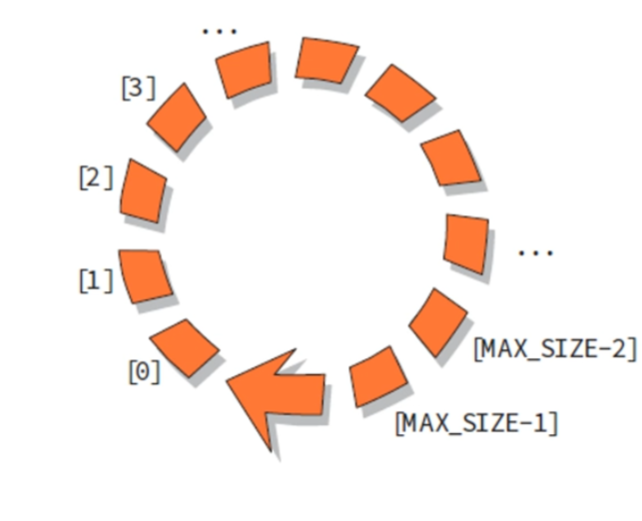
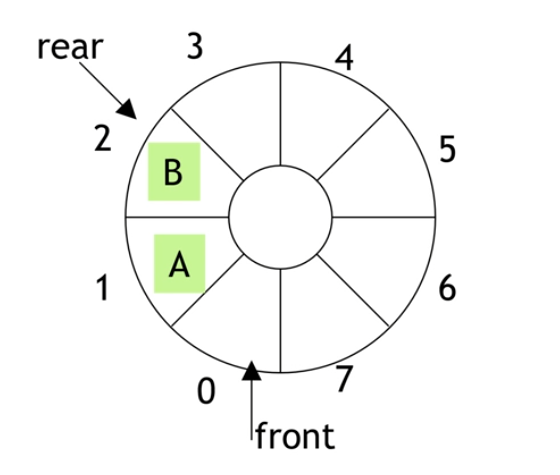
큐의 전단과 후단을 관리 하기 위한 2개의 변수 필요
- front : 첫번째 요소 하나 앞의 인덱스
- rear : 마지막 요소의 인덱스
선형 큐에 비해 포인터를 다시 앞쪽으로 끌고와서 큐 내용 삭제로 포인터가 뒤로 밀려나는게 없어져서, 메모리 용량을 효율적으로 사용할수 있음
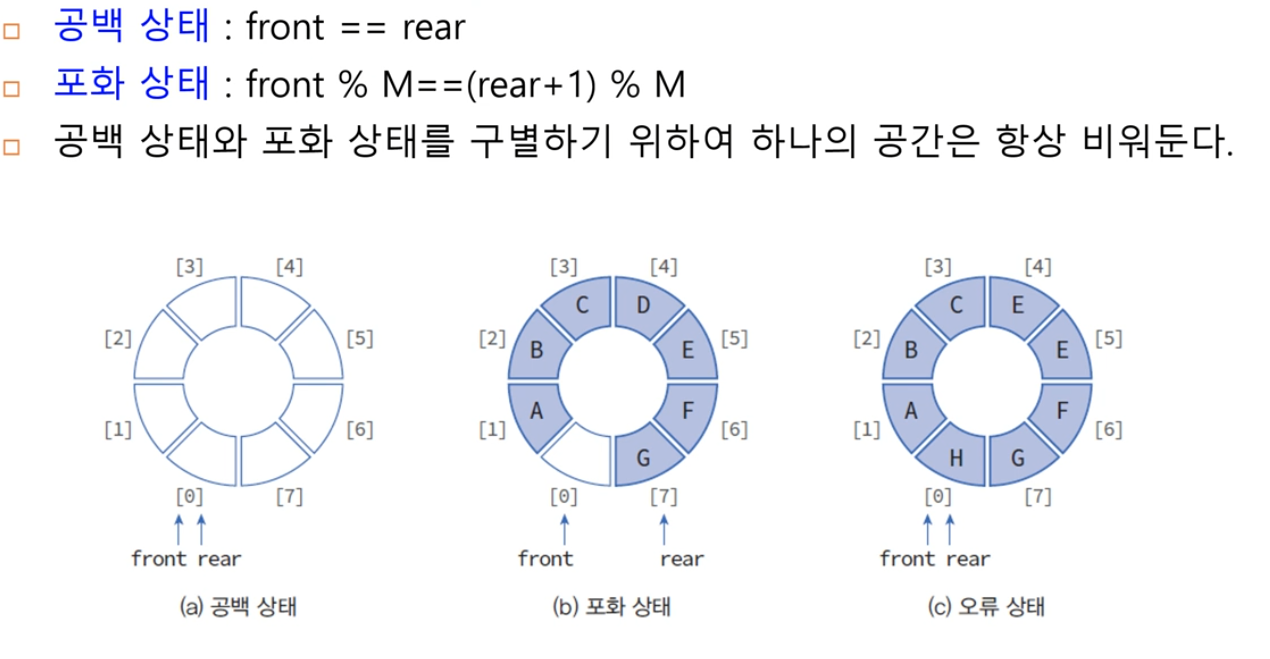
M은 현재 큐의 크기값
C를 이용한 원형큐 구현
더보기
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 5
//queue 구조체
typedef int element;
typedef struct {
int front;
int rear;
element data[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
} QueueType;
//에러 메세지 출력
void error(const char* message) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", message);
exit(1);
}
//초기화
void init_queue(QueueType* q) {
q->front = q->rear = 0;
}
int is_full(QueueType* q) {
return ((q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE == q->front);
}
int is_empty(QueueType* q) {
return (q->front == q->rear);
}
// 원형 QUEUE 타입 출력 함수
void queue_print(QueueType* q) {
printf("QUEUE(front=%d rear = %d) =", q->front, q->rear);
if (!is_empty(q)) {
int i = q->front;
do {
i = (i + 1) % (MAX_QUEUE_SIZE);
printf("%d | ", q->data[i]);
if (i == q->rear)
break;
} while (i != q->front);
}
printf("\n");
}
void enqueue(QueueType* q, int item) {
if (is_full(q)) {
error("큐가 포화 상태입니다.");
}
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
q->data[q->rear] = item;
}
element dequeue(QueueType* q) {
if (is_empty(q)) {
error("큐가 공백상태입니다");
}
q->front = (q->front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
return q->data[q->front];
}
int main(void) {
QueueType queue;
int element;
init_queue(&queue);
printf("데이터 추가 단계\n");
while (!is_full(&queue)) {
printf("정수를 입력하세요 :");
scanf_s("%d", &element);
enqueue(&queue, element);
queue_print(&queue);
}
printf("큐는 포화상태 입니다.\n\n");
printf("데이터 삭제 단계\n");
while (!is_empty(&queue)) {
element = dequeue(&queue);
printf("꺼내진 정수 : %d\n", element);
queue_print(&queue);
}
printf("큐는 공백상태입니다.\n");
return 0;
}
큐의 응용 : 버퍼
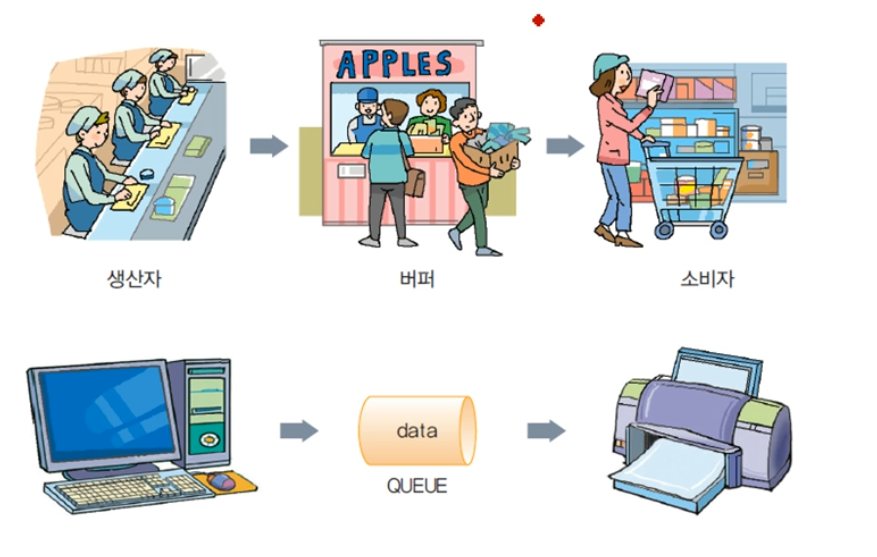
큐에 대한 기본적 이해를 가지도록 하자
원형 큐에 대한 front rear의 차이점, 큐의 응용 용도를 파악하자
느낀점 : 스택과는 다르게 큐는 선입 선출 방식이다. 이걸 알아두자.
'이론공부 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자료구조 공부#13 (연결리스트) (0) | 2021.04.13 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조 공부#12 (덱) (0) | 2021.04.09 |
| 자료구조 공부#10 (수식의 계산) (0) | 2021.03.31 |
| 자료구조 공부#9 (스택) (0) | 2021.03.27 |
| 자료구조 공부#8 (포인터) (0) | 2021.03.26 |
